문제 출처
SW Expert Academy [D2] 두 개의 숫자열
https://swexpertacademy.com/main/code/problem/problemDetail.do?contestProbId=AV5PpoFaAS4DFAUq
SW Expert Academy
SW 프로그래밍 역량 강화에 도움이 되는 다양한 학습 컨텐츠를 확인하세요!
swexpertacademy.com
예외 발생
unreported exception IOException; must be caught or declared to be thrown
예외 원인
BufferedReader 사용 시 IOException에 대한 예외 처리가 필요함

기본적인 예외의 경우. Checked Exception과 Unchecked Exception으로 구분할 수 있다.
Checked Exception의 경우 명시적인 예외 처리가 필요하다. 예외 처리를 하지 않을 경우, 컴파일 되지 않는다. 하지만 Unchecked Exception의 경우 컴파일은 가능하지만 예외가 발생할 경우 프로그램이 정상적으로 실행되지 않는다.
- checked Exception
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = br.readline();
}
}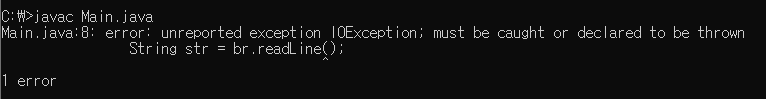
checked Exceptiond의 경우 예외 처리가 되지 않으면 컴파일 되지 않는다.
- Unchecked Exception
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println(array[i]);
}
}
}
Unchecked Exception 중 하나인 ArrayIndexOutofBoundsException 오류가 발생하도록 코드를 짰다.
cmd에서 실행해볼 경우, 컴파일은 되지만 실행시키면 Exception이 발생하였다고 뜬다.

해결 방안
1. throws IOException
import java.io.IOException;
public class Solution{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = br.readLine();
}
}
2. try-catch
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Study{
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = br.readLine();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
문제 해결 코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int testCase = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
for (int t = 0; t < testCase; t++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int[][] array = new int[2][];
array[0] = new int[N];
array[1] = new int[M];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < array[i].length; j++) {
array[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
int longIdx = (N >= M) ? 0 : 1;
int shortIdx = 1 - longIdx;
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < array[longIdx].length - array[shortIdx].length + 1; i++) {
int sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < array[shortIdx].length; j++) {
sum += array[shortIdx][j] * array[longIdx][i + j];
}
max = (sum > max) ? sum : max;
}
System.out.printf("#%d %d\n", t + 1, max);
}
}
}'Backend > Java-Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] 클래스.toString()을 public으로 선언해야 하는 이유 (1) | 2024.01.18 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 백준 1244번 - 스위치 켜고 끄기 (1) | 2024.01.17 |
| [Java] ArrayList와 LinkedList의 구현을 통한 성능 비교 (2) | 2023.11.25 |
| [알고리즘] 알고리즘 성능을 분석하는 상환 분석 (Amortized Analysis) (0) | 2023.11.22 |
| [Java] 추상클래스와 인터페이스의 비교 (1) | 2023.10.17 |


